NalkaRenergy's Hydrogen Fuel Technology
What are hydrogen stations and how do they work?

reference taken from google
Green hydrogen is one of the great alternatives in terms of sustainable mobility, and for this hydrogen stations, or hydrogen pumps, which function as a refuelling station for this fuel, are necessary. The aim is for India to have a network of more than 100 hydrogen stations by 2030.
Green hydrogen, obtained by electrolysis from renewable electricity – which separates hydrogen from the oxygen present in water – is positioned as one of the most important alternatives to traditional energy resources and a key element in the drive towards decarbonisation of transport and sustainable mobility.
Hydrogen is the most common chemical element in nature and hydrogen-powered vehicles have been available for more than ten years, so the next step is to use hydrogen from renewable electricity, i.e. green hydrogen.
The main advantages of this type of vehicle are that they offer a greater level of autonomy and less dependence on the battery and, unlike traditional electric vehicles, refuelling times are similar to those of combustion vehicles. However, for this to become a reality, the network of hydrogen stations needs to be expanded.
HOW DOES A HYDROGEN STATION WORK?
The process of refuelling at a hydrogen station is not very different from that of a conventional petrol station, although there are some details that make the experience a little different. This is because hydrogen is supplied at high pressure and, as it is an extremely volatile gas, the connection between the vehicle’s receptacle or connection point and the pump must be watertight.
The hydrogen is pumped into the vehicle’s fuel tank, which powers the fuel cell that generates the electricity needed to drive the vehicle. The only waste product produced is water vapour, which is expelled through the exhaust pipe.
Unlike conventional filling stations, hydrogen is sold by the kilo, not by the litre, and the refuelling time for a conventional bus – which usually has a capacity of between 30 and 37.5 kilos – is no more than 12 minutes. And on the question of how much a hydrogen bus consumes, it is estimated at approximately 8 kilos per 100 kilometres, so the range of hydrogen vehicles currently on the market would be around 400 kilometres.
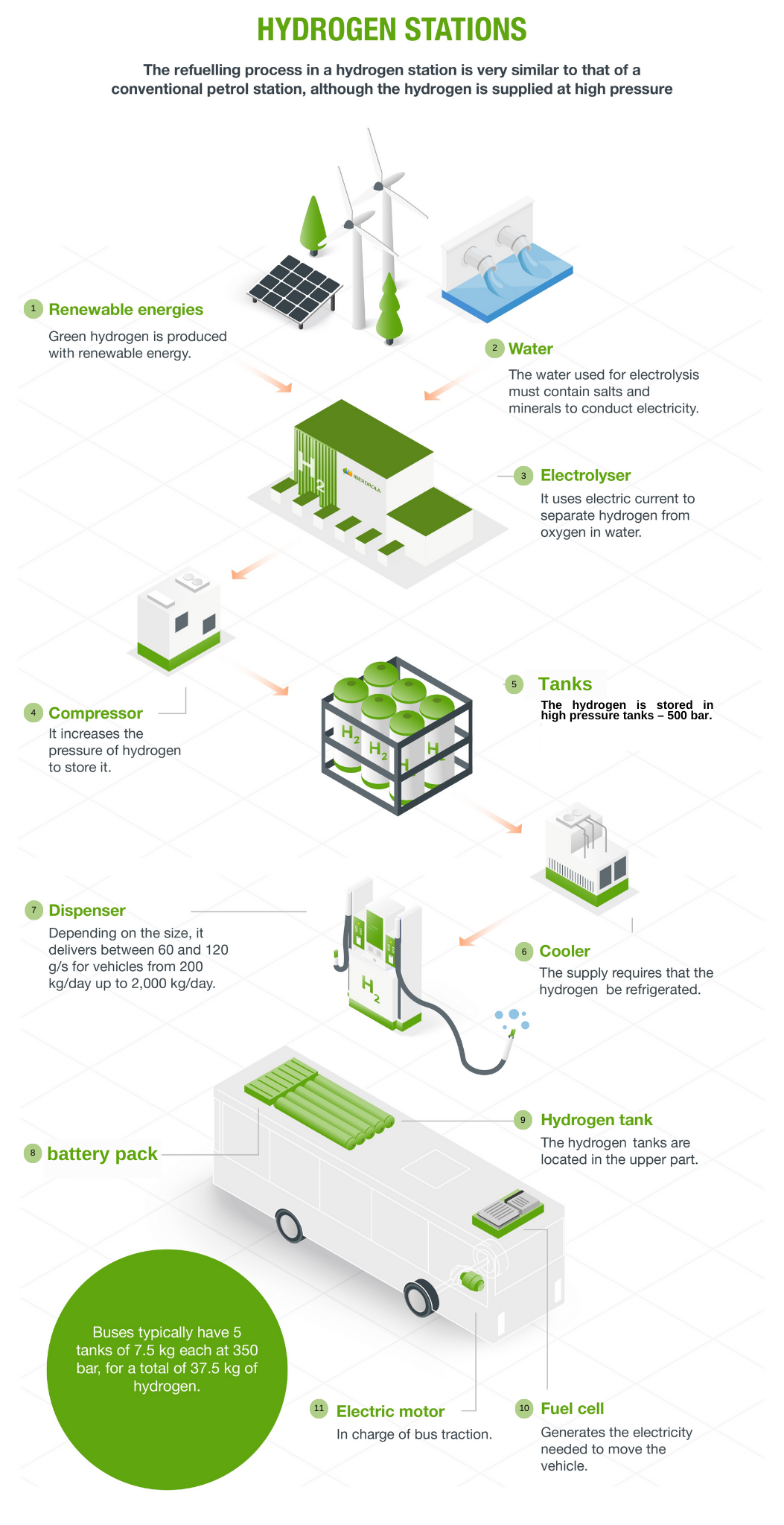
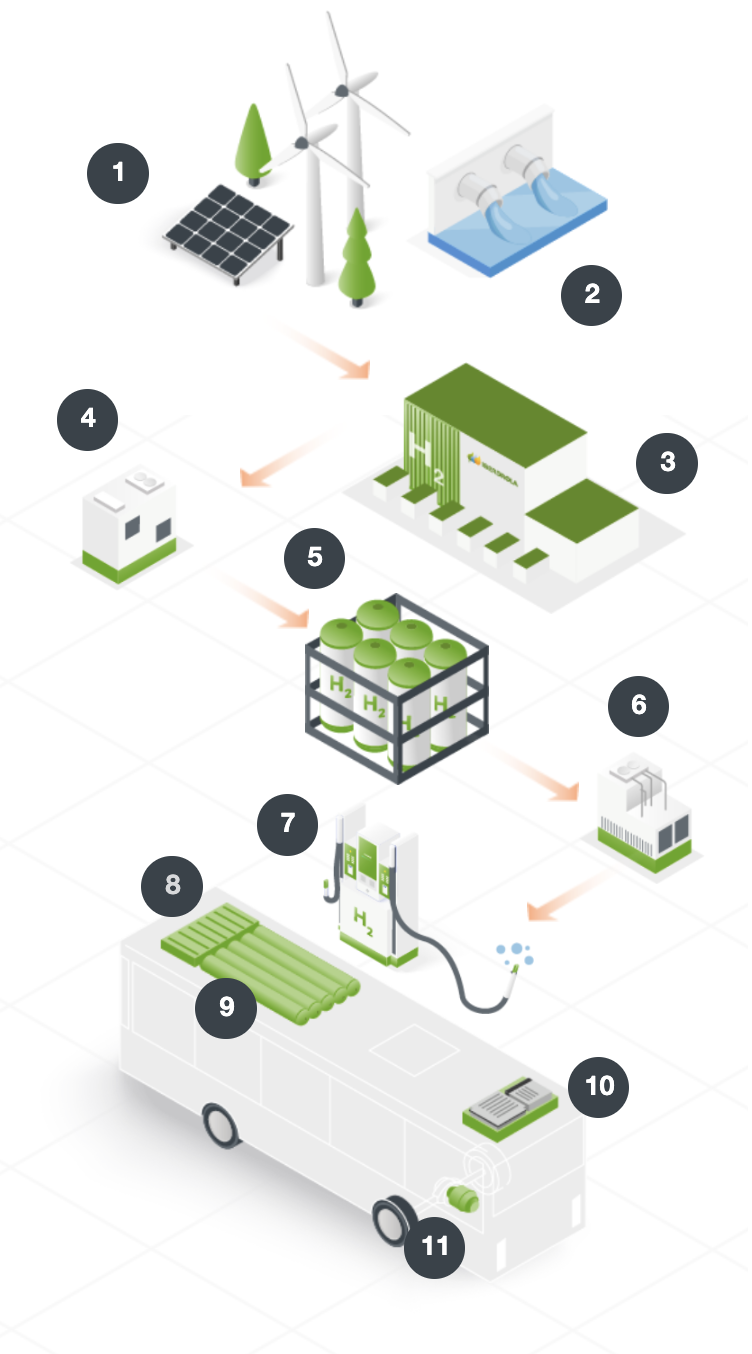
Renewable energies
Green hydrogen is produced with renewable energy.
Water
The water used for electrolysis must contain salts and minerals to conduct electricity
Electrolyser
It uses electric current to separate hydrogen from oxygen in water
Compressor
It increases the pressure of hydrogen to store it
tanks
The hydrogen is stored in high pressure tanks – 500 bar.
Cooler
The supply requires that the hydrogen be refrigerated
Dispenser
Depending on the size, it delivers between 60 and 120 g/s for vehicles from 200 kg/day up to 2,000 kg/day
battery pack
Hydrogen tank
The hydrogen tanks are located in the upper part
Fuel cell
Generates the electricity needed to move the vehicle
Electric motor
In charge of bus traction.
